Why Healthcare industry needs better Data Security?

The Importance of Data Privacy in Healthcare
In 2023, healthcare data breaches have affected over 112 million individuals, making healthcare the most targeted industry for cyber attacks. These breaches have resulted in the compromise of various types of personal information, such as names, dates of birth, social security numbers, Medicaid and health plan identification numbers, addresses, phone numbers, and credit card numbers.
Data privacy is crucial in healthcare to protect and maintain the confidentiality of patients' personal and sensitive information. It plays an important role in building trust between patients and healthcare providers, ensuring the safety of patients' personal records. Furthermore, data privacy is essential for preserving the integrity and accuracy of patient records, as they may be vulnerable to manipulation in the event of a breach.
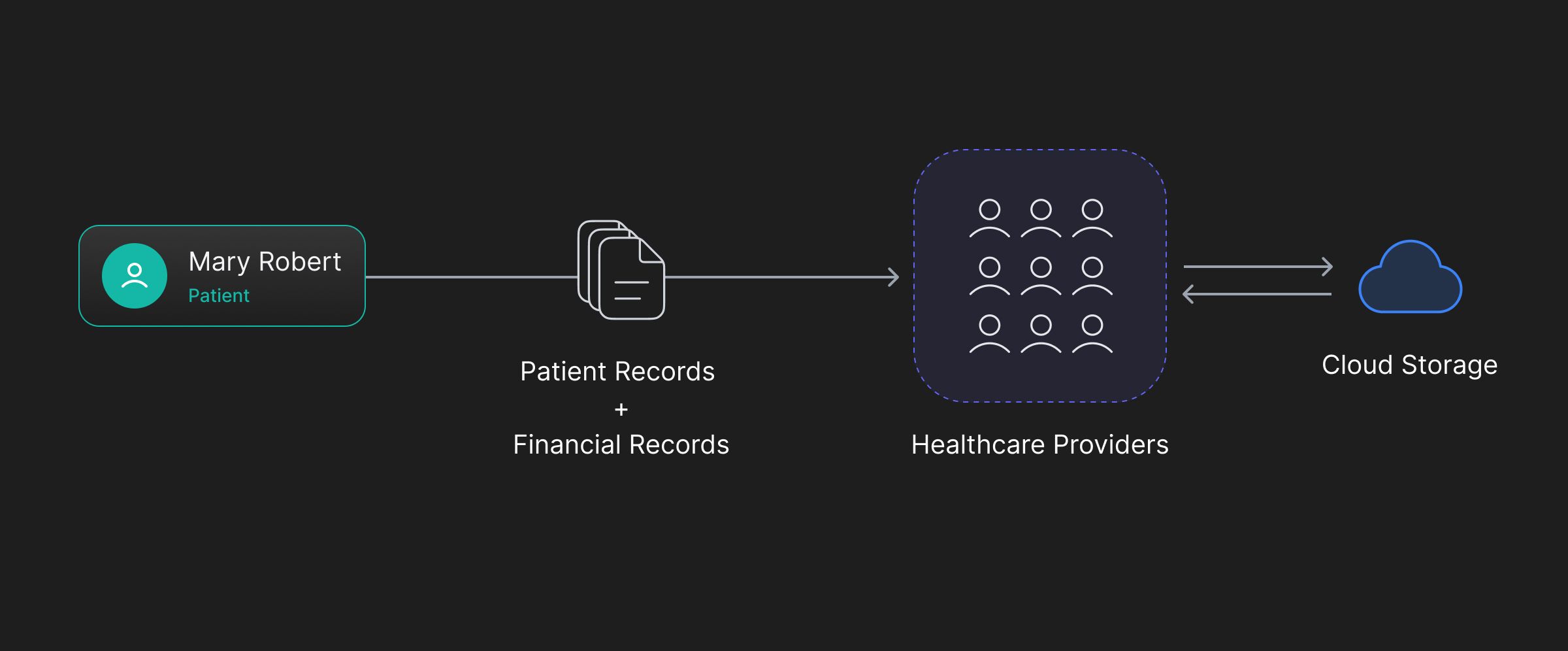
HIPAA, a framework for data protection in the healthcare industry, ensures that healthcare organizations follow stringent security protocols when storing and processing personal data. It sets standards to protect the privacy of identifiable health information and regulates the maintenance of protected health information by complying entities. HIPAA also grants patients control over their medical records, superseding less protective privacy laws.
Understanding HIPAA: Regulations and Standards for Data Protection
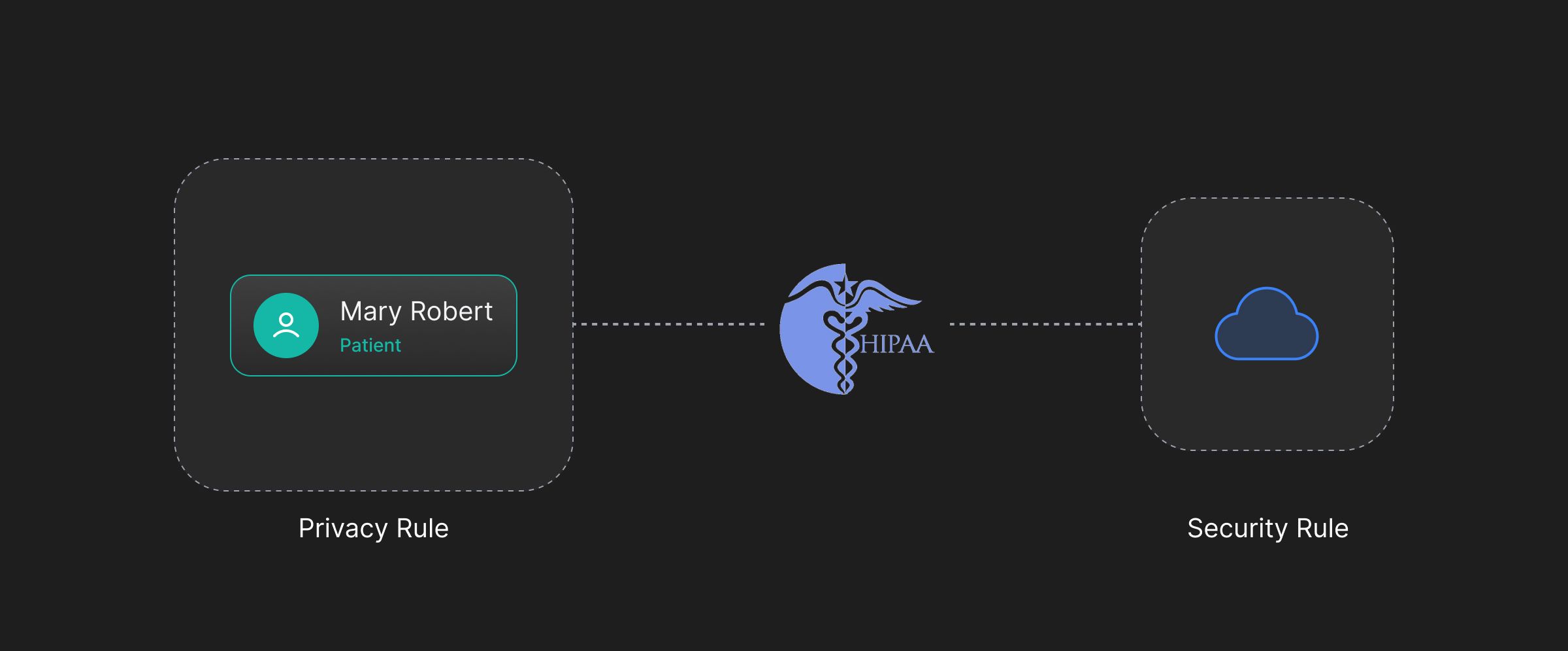
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), introduced in 1996, is a comprehensive framework for data protection in the healthcare industry. It sets out to create standards that protect the privacy of identifiable health information. HIPAA covers several areas relating to health data and consists of two main rules: the Privacy Rule and the Security Rule.
The Privacy Rule - The HIPAA Privacy Rule focuses on the right of the user to control what happens to their health data. It covers the administration, physical, and technical aspects of data protection. The Privacy Rule sets a baseline of protection for certain individually identifiable health information and regulates protected health information maintained by covered entities.
This rule requires healthcare organizations to implement physical and technical measures to protect the confidentiality of patient data. This includes using secure servers and encryption methods to safeguard electronic health records.
The Security Rule - The HIPAA Security Rule covers data integrity, confidentiality, and availability of data. It ensures that appropriate safeguards are in place to protect electronic health information.
This rule requires healthcare organizations to ensure the integrity and availability of data. This means implementing measures such as access controls and regular monitoring to protect patient information from unauthorized access or breaches.
While HIPAA is a crucial aspect of data protection in healthcare, it is not the only regulation in place. The HITECH Act, for example, covers vendors of personal health records and third-party service providers not covered by HIPAA. Additionally, federal and state privacy laws require healthcare providers to obtain patients' written consent before disclosing their health information to other people and organizations.
Overall, HIPAA is a comprehensive framework that focuses on protecting the privacy and security of health data. It sets standards, rules, and protocols to ensure that individuals have control over their health information and that appropriate safeguards are in place to protect it.
Data Analysis in Healthcare: Potential Benefits and Challenges
Big data refers to large and complex datasets requiring sophisticated technology and methods for storage, analysis, and interpretation. In healthcare, it refers to the use of large datasets from thousands (or millions) of patients to analyze and extract valuable insights.
By researching better prevention and detection methods, Big Data Analytics aims to improve the health and condition of patients by identifying new approaches to healthcare, enhancing patient care, and reducing costs of treatment. Big data analysis in healthcare has the potential to bring benefits to medical facilities, healthcare stakeholders, and the healthcare industry as a whole.
Challenges and Risks associated with Sensitive Data
Healthcare workers regularly face challenges with data capture, storage, and analysis. These challenges arise due to the large amount of information that needs to be handled and which is in constant flux. Additionally, challenges with handling diverse sources of data and integrating and storing it introduces more complexity. Effectively navigating through these challenges might not just improve the healthcare services of the organization, but also help build reputation and lead to financial benefits.
The risks associated with handling sensitive data are critical as it can compromise patient information. This can lead to the unauthorized access or disclosure of personal information such as names, birth dates, social security numbers, phone numbers, and addresses. Healthcare is a hot target for cyberattacks, and adhering to regulatory guidelines and implementing a better security posture can go a long way.
Data Breaches in Healthcare: Implications and Prevention Measures
Major healthcare organizations like Advocate Health Care, Banner Health, Medical Informatics Engineering, and Trinity Health experienced breaches in 2023. Additionally, HCA healthcare was fined $555 million by the Health and Human Services Department for a breach to their OCR in July 2023.
Healthcare data breaches continue to pose significant challenges for healthcare organizations, emphasizing the importance of securing their infrastructure. Some major implications of data breaches in healthcare include:
- Compromised personal information - Compromised SPI can lead to identity theft and financial fraud.
- Violation of data protection standards - Violations of regulatory standards can result in legal consequences and fines.
- Impact on healthcare providers and plans - Data breaches can lead to a loss of trust from patients and damage reputation.
- Increased cyberattacks - Hackers may target healthcare organizations that have already experienced breaches.
- Negative impact on patient care - Data breaches can disrupt healthcare operations and lead to a loss of patient trust.
- Financial implications - Significant potential financial losses for healthcare organizations, including fines, legal fees, and costs associated with remediation and recovery efforts.
It’s best to prepare for these attacks before hand rather than recover from them. Some standard ways organizations maintain a robust security posture in the healthcare industry are as follows.
Prevention Measures
- Access Management - Implementing strong access control policies allows you to effectively manage roles and restrict privileges to privileged users and limited resources. Managing access is the initial step in securing your infrastructure, as many data breaches stem from compromised credentials.
- Real-Time Monitoring - Constantly monitoring access activity, deploying policies to detect any violations to sensitive data, and automating response pipelines are the next steps to secure the ever-growing data reserves.
- Data Encryption - To protect sensitive information such as social security numbers and bank account information, it is important to implement strong data encryption measures. This will help strengthen cyber resilience in healthcare organizations. Additionally, encryption allows for the secure sharing of patient data between healthcare providers and other entities offering health services.
- HIPAA (and other regulations) - Follow the standards outlined in the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) for data protection. Train and educate the team on HIPAA-compliant content management systems to protect patients' confidential health information. This will ensure the organization remains compliant at all times.
- Third Party Compliance - Ensure third-party vendors and partners comply with mandatory financial regulations and regularly assess their security posture. Only sharing data with compliant organizations can create better security posture and save unnecessary repercussions like the data breach of Target.
Closing the Gap: Regulating Consumer Health Data in line with HIPAA
The EU Data Protection Regulation GDPR tries to balance patients' privacy while ensuring that patients' data can be shared for healthcare and research purposes. Additionally, Washington’s “My Health, My Data Act” increases protections regarding the collection, sharing, and sale of health data without the consumers' knowledge. It is important for healthcare providers to follow federal and state privacy laws, which require obtaining patients' written consent before disclosing their health information to other people and organizations. Providers should also make every effort to limit the potential disclosure of private information.
To ensure best practices with managing consumer health data in line with HIPAA, some best practices are listed below—
- Understand the HIPAA regulations - Familiarize yourself with the regulations outlined in HIPAA, which sets out the framework for data protection and privacy of health information.
- Implement data protection standards - Ensure that data protection standards outlined in the Act are followed. This includes safeguarding protected health information maintained by covered entities and complying with the Privacy Rule.
- Increase protections regarding the collection, sharing, and sale of health data - The My Health, My Data Act and the CTDPA amendment seek to enhance protections for consumer health data in addition to HIPAA.
- Give patients control over their health data - HIPAA grants patients the right to control what happens to their health data. Ensure that patients have access to their electronic protected health information (ePHI) as required by the HITECH Act.
- Comply with breach notification protocols - Follow the breach notification protocol specified under HIPAA in the event of a data breach. This includes notifying affected individuals and taking steps to mitigate the impact of the breach.
- Stay informed about federal and state privacy laws - Be aware of federal and state privacy laws that may require obtaining patients' written consent before disclosing their health information to others.
- Use HIPAA-compliant content management systems - Train your team on how to use HIPAA-compliant content management systems to protect patients' confidential health information.
The Role of Technology in Ensuring Data Privacy in Healthcare
Technology has played a key role in ensuring data privacy in healthcare. It is important for protecting confidential patient information and minimizing the risk of a breach. By updating security systems as technology advances, healthcare providers can safely manage patient data between different entities providing health services. Additionally, technology enables the use of big data tools, which can help healthcare institutions analyze and utilize large amounts of data to enhance patient care and improve the quality of life. The HIPAA Privacy Rule also covers the administration, physical, and technical aspects of data protection, emphasizing the right of the user to control what happens to their health data. With time, regulations will only become more stringent, and following best practices is the way out to always be on top of compliance.
 SOC2 Type II
SOC2 Type II

